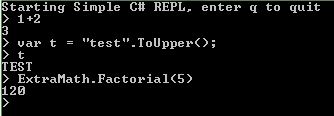
Here is the full code (github) of my simple REPL. If you end a statement with ';' then it will run without returning an output, use this when you want to create objects . If you omit the ';' then the expression is evaluated and the result printed. Note that I added a reference to my program to the evaluator in order to be able to call the Factorial function. Also fon't to forget to run the necesssary Using statements.
// Install-Package Mono.CSharp using System; using System.Reflection; using Mono.CSharp;
namespace SimpleREPL { public class ExtraMath { public static int Factorial(int n) { // naive implementation but fast enough for small n int result = 1; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { result *= i; } return result; } } internal class Program { private static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Starting Simple C# REPL, enter q to quit"); var evaluator = new Evaluator(new CompilerContext( new CompilerSettings(), new ConsoleReportPrinter())); evaluator.ReferenceAssembly(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly()); evaluator.Run("using System;"); evaluator.Run("using SimpleREPL;"); while (true) { Console.Write("> "); var input = Console.ReadLine(); input = input.TrimStart('>', ' '); if (input.ToLower() == "q") { return; } try { if (input.EndsWith(";")) { evaluator.Run(input); } else { var output = evaluator.Evaluate(input); Console.WriteLine(output); } } catch { Console.WriteLine("Error in input"); } } } } }
No comments:
Post a Comment